Neoprene is a versatile synthetic rubber that has found widespread use across various industries due to its exceptional properties and durability. Developed in the 1930s by DuPont scientists, Neoprene, also known as polychloroprene, is a family of synthetic rubbers produced through the polymerization of chloroprene. This material boasts good chemical stability and flexibility over a wide temperature range, making it ideal for a multitude of applications[1][2].
Properties and Applications
Neoprene exhibits remarkable resistance to degradation, making it suitable for demanding applications like gaskets, hoses, and corrosion-resistant coatings. Its versatility extends to being used in electrical insulation, medical gloves, liquid membranes, automotive fan belts, and more. Due to its tolerance of extreme conditions, Neoprene is even utilized in lining landfills[1].
Industrial and Consumer Uses
The material’s chemical inertness has led to its application in industrial settings for corrosion-resistant coatings and sealing gaskets, especially in electrical applications. In consumer products, Neoprene is commonly found in safety equipment like gloves for its oil, chemical, and water resistance. It is also prevalent in marine gear such as wetsuits and diving suits due to its water and thermal resistance[3].
Manufacturing Process
Neoprene is produced through free-radical polymerization of chloroprene. The material can be manufactured as solid rubber or in latex form. The production process involves crosslinking individual polymer strands using bifunctional nucleophiles and metal oxides. Neoprene foam, either closed-cell or open-cell, is created by foaming the rubber with nitrogen gas to provide insulation[1][4].
Grades of Neoprene Rubber
Various grades of Neoprene rubber are available to cater to different application requirements. These include Commercial Grade Neoprene Rubber, British Standard BS2752 Neoprene Rubber, Expanded Neoprene/EPDM Closed-Cell Sponge Rubber, Flame Retardant Neoprene Rubber, and Neoprene/Nylon Insertion Diaphragm Rubber. Each grade offers specific advantages based on properties like tensile strength and tear resistance[2].
In conclusion, Neoprene’s history as a groundbreaking synthetic rubber developed by DuPont has paved the way for its extensive use in diverse industries ranging from automotive to marine applications. Its unique properties such as resistance to degradation and flexibility have made it a sought-after material for various commercial and industrial purposes.
[1] Wikipedia – Neoprene
[2] Delta Rubber – What is Neoprene Rubber?
[3] Vedantu – Neoprene: Introduction, Properties, Types & Uses
[4] Sewport – What is Neoprene Fabric: Properties & Applications
- Neoprene – Wikipedia
Neoprene, also known as polychloroprene, is a synthetic rubber with good chemical stability and flexibility over a wide temperature range. It is used in various commercial applications such as laptop sleeves, orthopedic braces, electrical insulation, and automotive fan belts. The production of neoprene involves free-radical polymerization of chloroprene, and it is sold as solid rubber or in latex form. The material is also used in the manufacture of dishwashing gloves and has found its way into fashion design. However, some people are allergic to neoprene, and precautions need to be taken due to potential dermatitis from its production residues. - Neoprene – Simple English Wikipedia
Neoprene is a synthetic polymer resembling rubber, resistant to oil, heat, and weathering. It is the trade name for a family of synthetic rubbers produced by the polymerization of chloroprene. - Neoprene (CR) – Britannica
Neoprene, also known as polychloroprene or chloroprene rubber, is a synthetic rubber valued for its high tensile strength, resilience, oil and flame resistance, and resistance to degradation by oxygen and ozone. It is used in various applications such as wire and cable insulation, hoses, belts, springs, flexible mounts, gaskets, and adhesives, where resistance to oil, heat, flame, and abrasion are required.
The provided URLs offer detailed information about neoprene, including its properties, production, and various applications.
Citations:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polychloroprene
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neoprene
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chloroprene
[4] https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neoprene
[5] https://www.britannica.com/science/neoprene
Neoprene (also polychloroprene) is a family of synthetic rubbers that are produced by polymerization of chloroprene. Neoprene exhibits good chemical stability and maintains flexibility over a wide temperature range. Neoprene is sold either as solid rubber or in latex form and is used in a wide variety of commercial applications, such as laptop sleeves, orthopaedic braces (wrist, knee, etc.), electrical insulation, medical gloves, liquid and sheet-applied elastomeric membranes or flashings, and automotive fan belts.
 A neck seal, wrist seal, manual vent, inflator, zip and fabric of a neoprene dry suit. The soft seal material at the neck and wrists is made from single backed closed-cell foam neoprene for elasticity. The slick unbacked side seals against the skin. The blue area is double-backed with knit nylon fabric laminated onto closed cell foamed neoprene for toughness. Some insulation is provided by the suit, and the rest by garments worn underneath.
| |
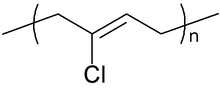 Chemical structure of the repeating unit of polychloroprene
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.127.980 |
| EC Number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 (solid) 0.1-0.3 g/cm3 (foam) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
English
Etymology
US, 1930s; genericized trademark for DuPont brand of polychloroprene.